System Settings is used to configure all the system related settings of the LogPoint.
Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the General tab.
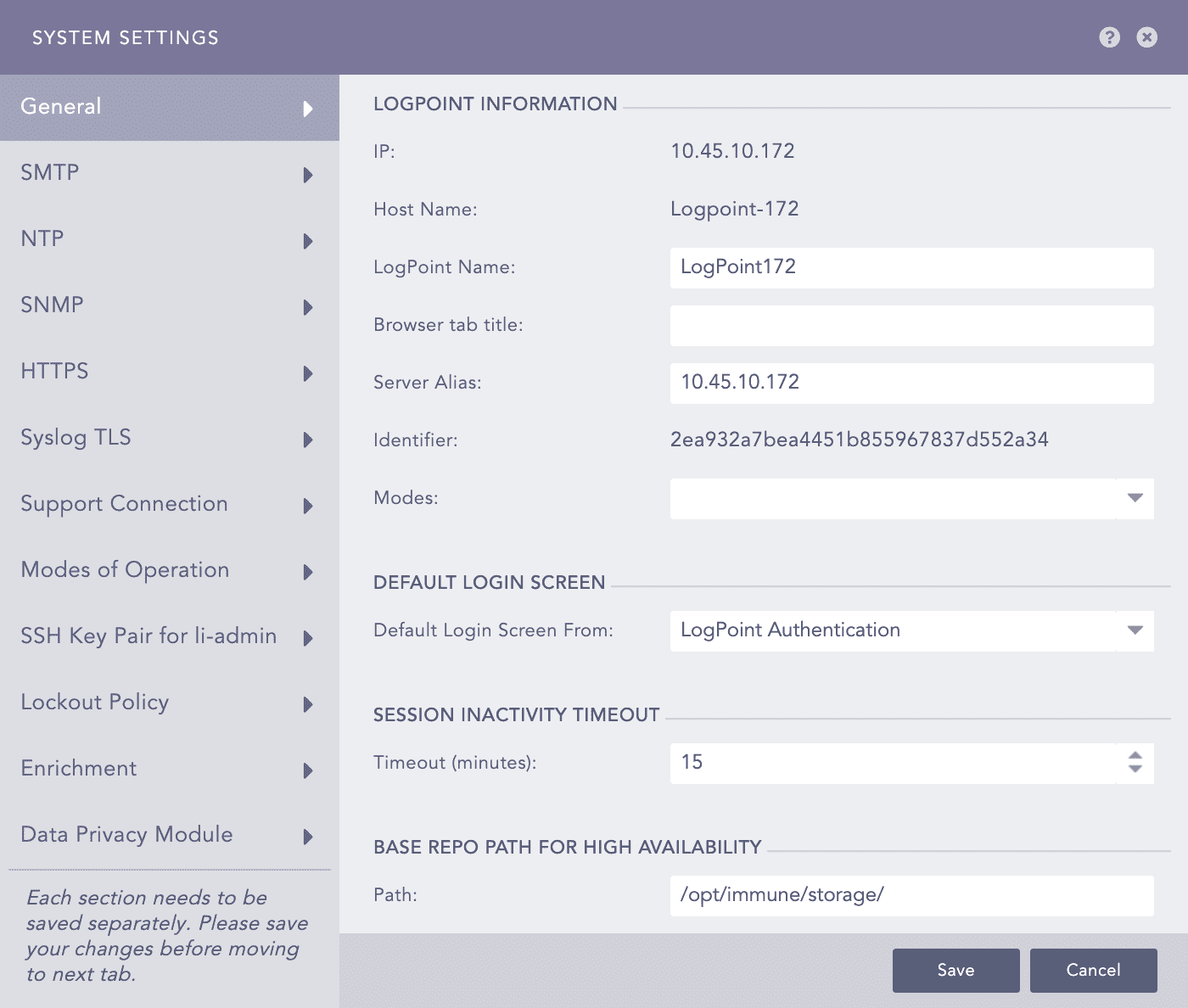
General - System Settings¶
Provide a LogPoint Name, a Browser tab title, and a Server Alias.
Note
The value entered in the Browser tab title is appended to the title of the tab.
Updating the Server Alias does not update the system IP Address or the DNS.
The Identifier is the unique value given to each LogPoint.
The Modes drop-down menu contains the options Search Head and Distributed LogPoint. Selecting either of these options does not have any effect on LogPoint. The Modes field is made available for future implementation of the LogPoint Director (Director Console).
Select the Default Login Screen for the LogPoint.
Provide the Timeout (minutes) period in the Session Inactivity Timeout sub-section. Users are logged out of the LogPoint after inactivity for the specified time-period.
Provide the Base Repo Path for High Availability to alter the default path /opt/immune/storage/. It is the base path for the repos from the remote machine.
Select either Collection Timestamp (col_ts) or Log Timestamp (log_ts) as per your requirement. The col_ts denotes the time when the log was collected in LogPoint, and the log_ts denotes the time when a device generated the log.
Choose the Over Scan Period (in minutes and a Time Zone. The overscan period is the extra period (apart from the selected period) in which LogPoint searches for logs. Both the col_ts and the log_ts fields are saved in UTC and displayed according to the selected time zone.
Note
The time conversion of log_ts occurs when a Normalization Policy is applied to the appropriate Collectors/Fetchers.
Depending on the selection made in the Apply Time Range On section, either log_ts or col_ts value is displayed on the top of each row of the search results. Similarly, the time displayed in the search graph may either be log_ts or col_ts depending on the selection made.
Both the log_ts and col_ts key-value pairs are displayed in the search results.
The Time Range is applied either on the col_ts or the log_ts across all the Distributed LogPoints.
Mark Add sequence numbers on log received from syslog collector to provide a sequence number to the syslogs. The number is assigned on a device per protocol basis to each log collected from the Syslog Collector.
Enable SOAR to enable incident investigation with Playbooks and Cases. Refer to the Getting Started with SOAR for details on LogPoint SOAR.
Note
Enabling or disabling SOAR may take some time depending on the available memory.
SOAR is always disabled in the LogPoint Collector and Syslog Forwarder modes.
Click Save.
SMTP is used to send e-mails from the LogPoint. The alert engine uses SMTP service to forward information. You need to configure the SMTP service before using the LogPoint to send e-mails.
Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the SMTP tab.
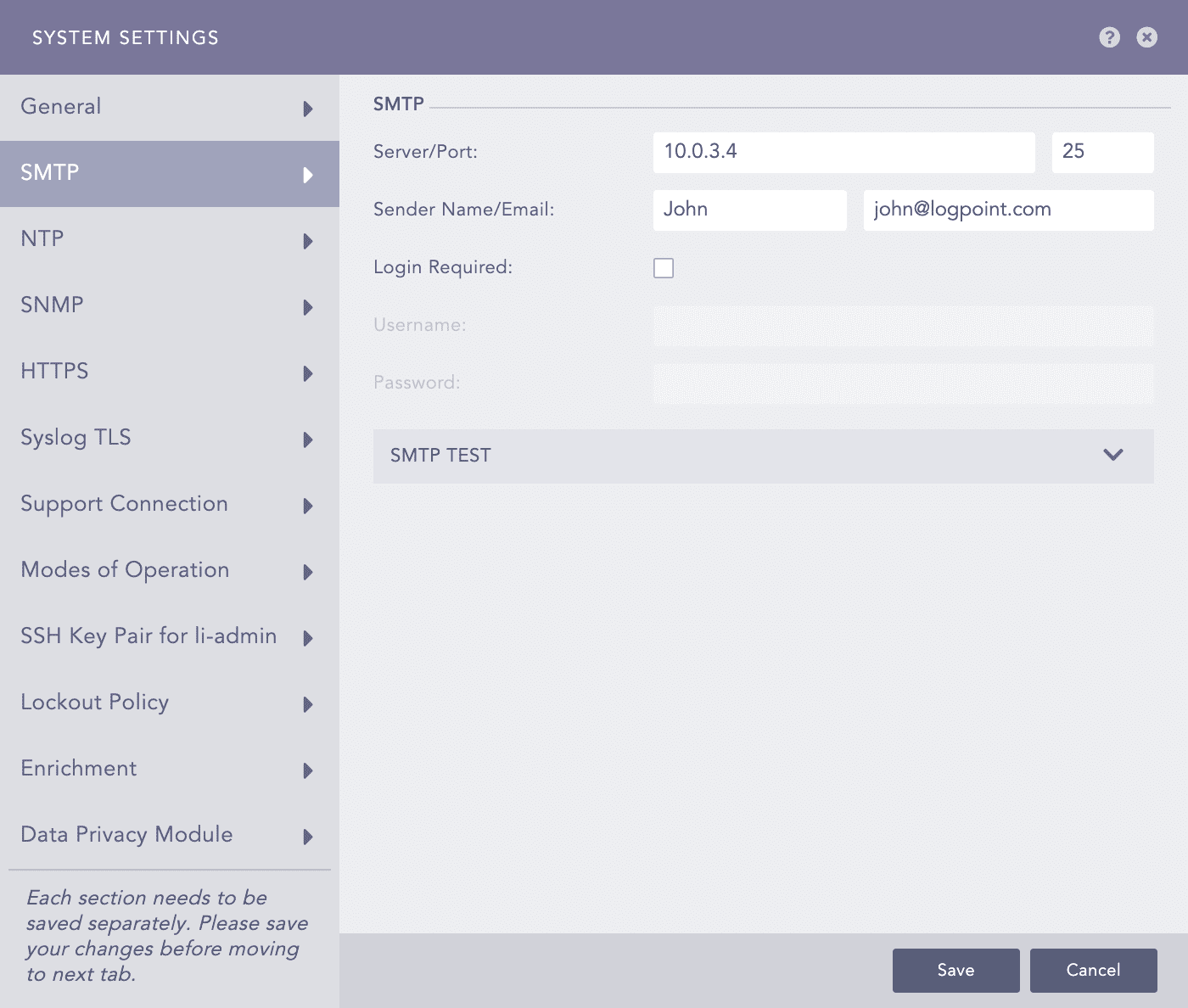
SMTP - System Settings¶
Provide the Server/Port.
Provide a Sender Name and an Email address.
If you enable the Login Required option, provide the Username and the Password.
Click Save.
To test the configuration, go through the following steps:
Click the SMTP Test section.
Enter the Subject of the test e-mail.
Provide an Email address.
Enter a Message.
Click Test SMTP.
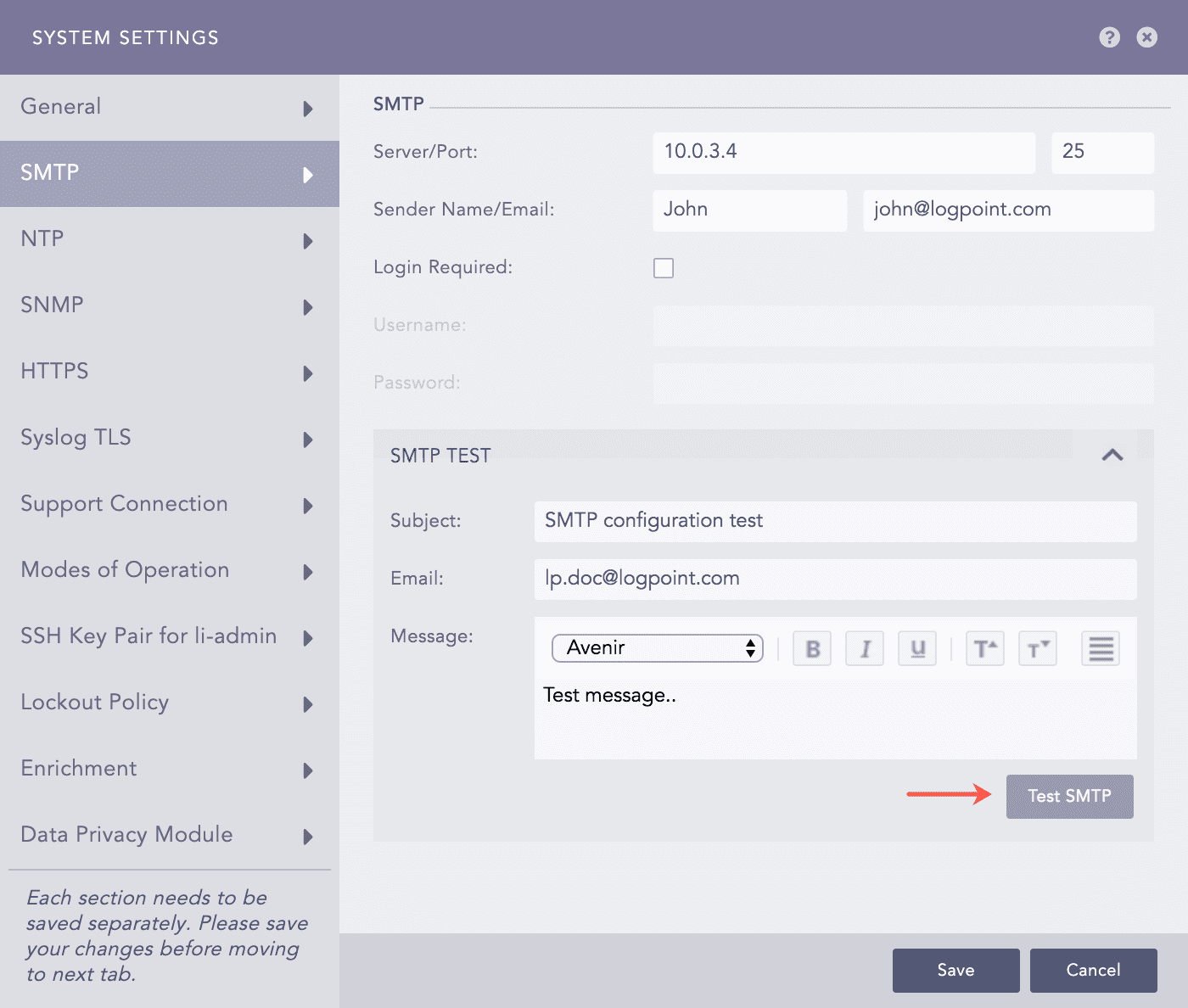
SNMP Test¶
Note
Configure the SMTP service before using the Data Privacy Module.
NTP synchronizes the time of your appliance with a network timeserver.
Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the NTP tab.
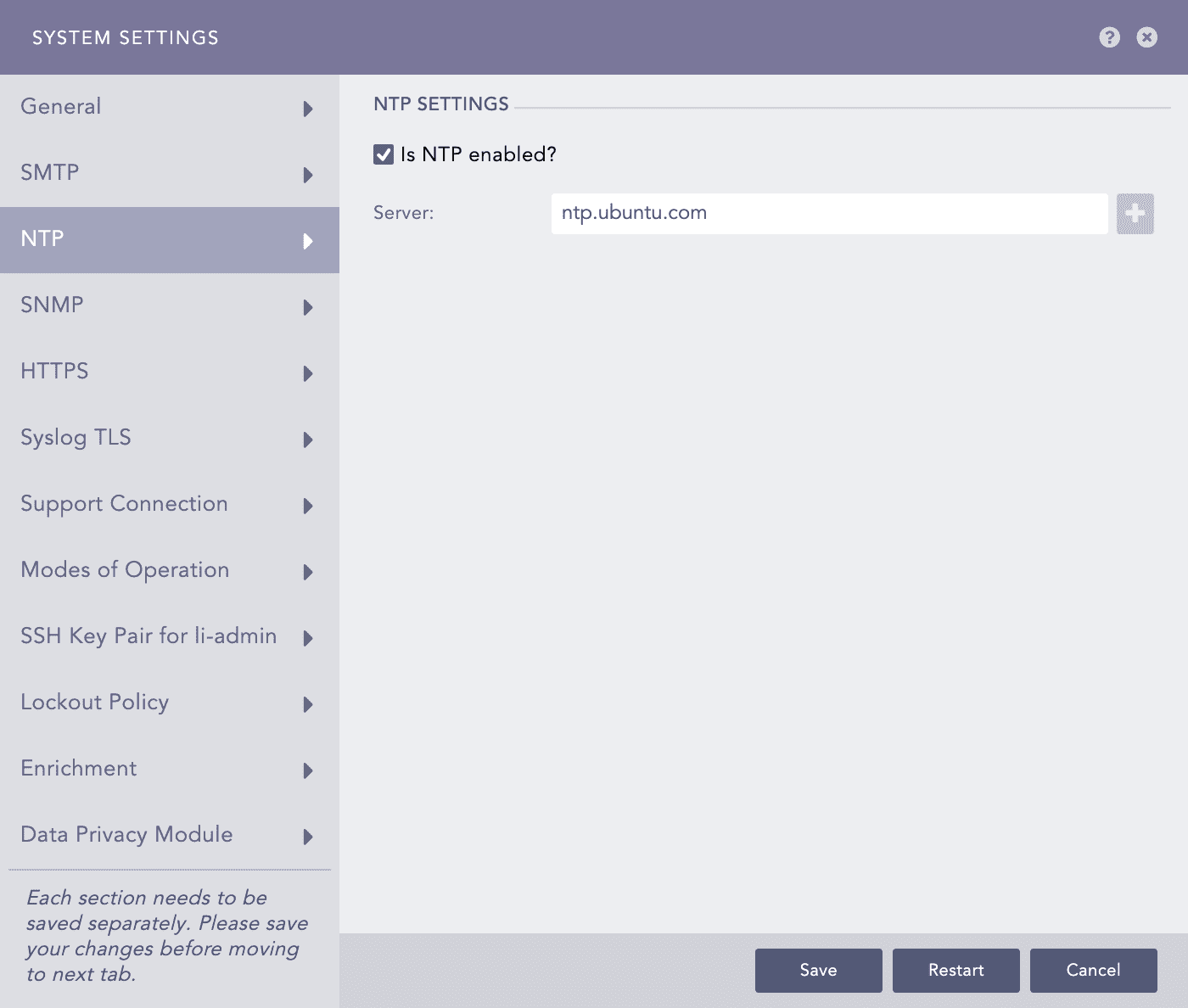
NTP - System Settings¶
Under the NTP Settings, check the Is NTP enable? option.
Provide the Server address. You can add multiple server addresses by clicking the plus icon.
Click Save.
If you enable the SNMP port, your LogPoint listens to the OIDs that are forwarded to the 161 port.
Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the SNMP tab.
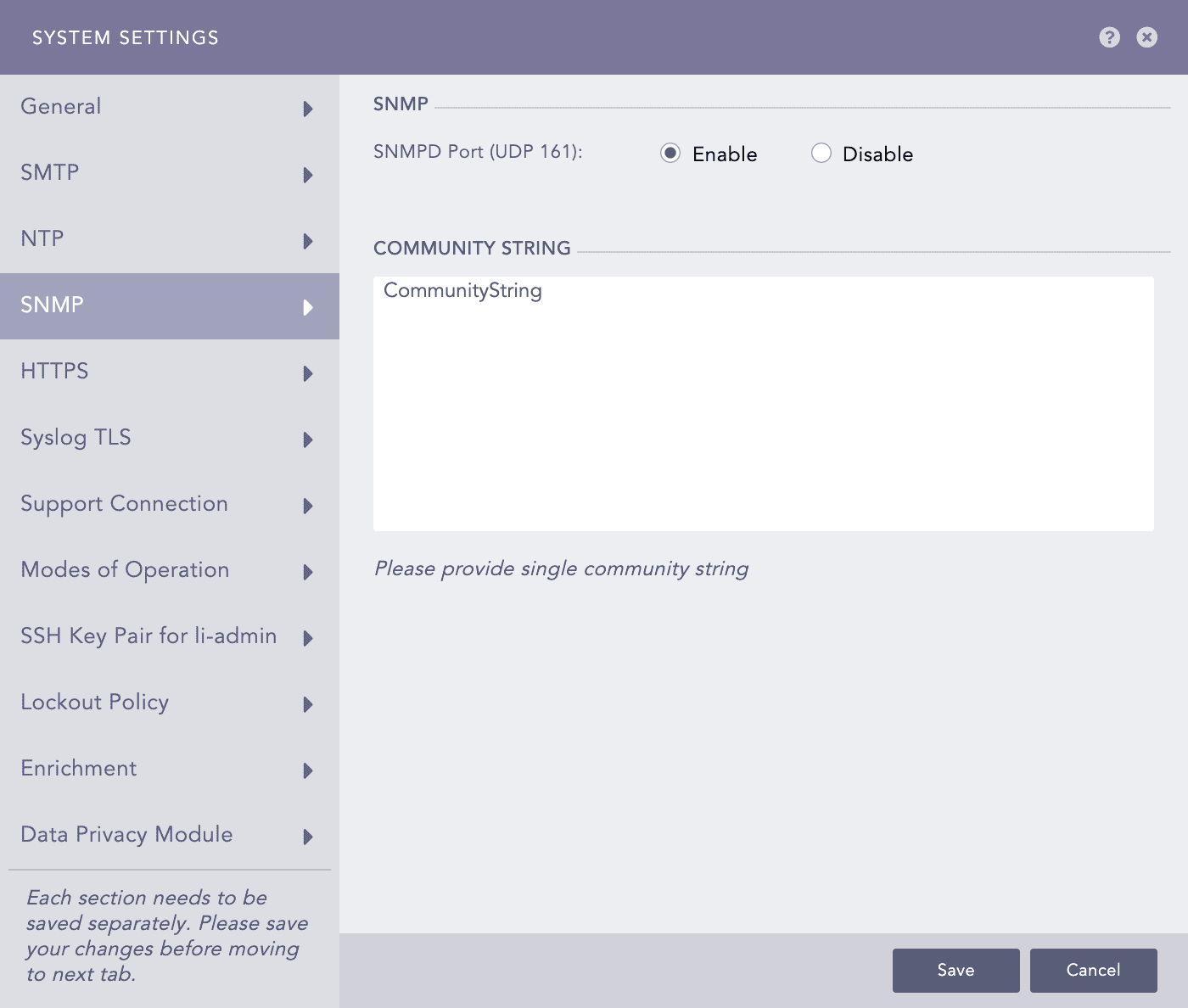
SNMP - System Settings¶
Choose to Enable or Disable the SNMPD(UDP 161) port.
Provide the Community String if you choose the Enable option.
Click Save.
Note
To get the exposed OID for the LogPoint, run the following snmpwalk command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public <ip_of_LogPoint>.
The HTTPS Service authenticates the LogPoint and prevents eavesdroppers from accessing the data in the network. HTTPS secures the server connection so LogPoint users can safely access the LogPoint from the Internet.
You must have a certificate and a key to enable the HTTPS option.
Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the HTTPS tab.
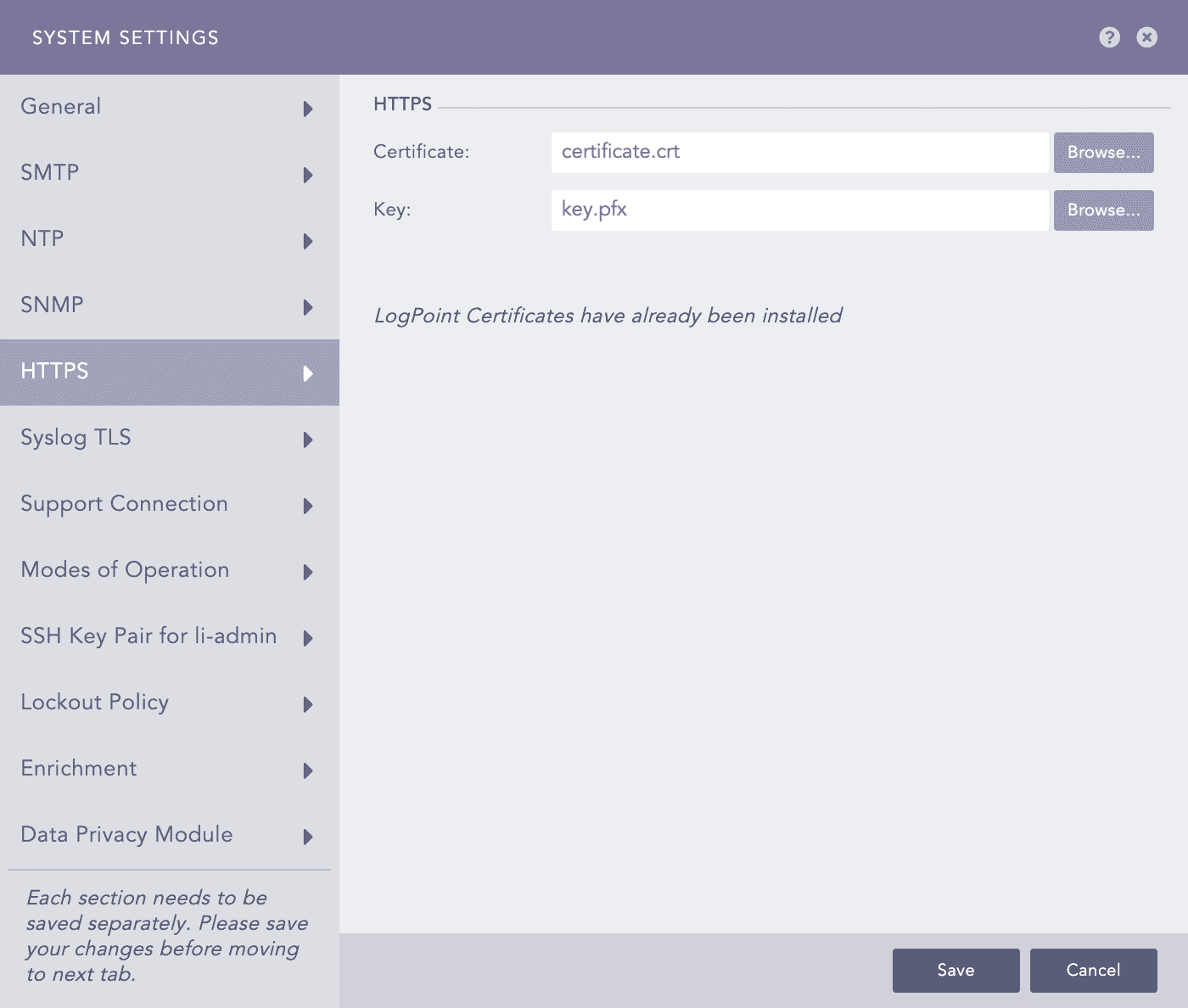
HTTPS - System Settings¶
Browse for the Certificate and the Key.
Click Save.
Note
The HTTPS certificate must be of PEM encoded x.509 standard.
The certificate file must have the CRT extension and the key file must have the KEY extension.
Upgrading to LogPoint v6.0.0 Patch is restricted if you have HTTPS certificates less than 2048 bits. The LogPoint certificates do not replace the existing user certificates of 2048 bits.
You can add a custom TLS certificate for log collection via Syslog. The added certificate is used by the Syslog collector to collect logs through TLS on port 6514.
Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the Syslog TLS tab.
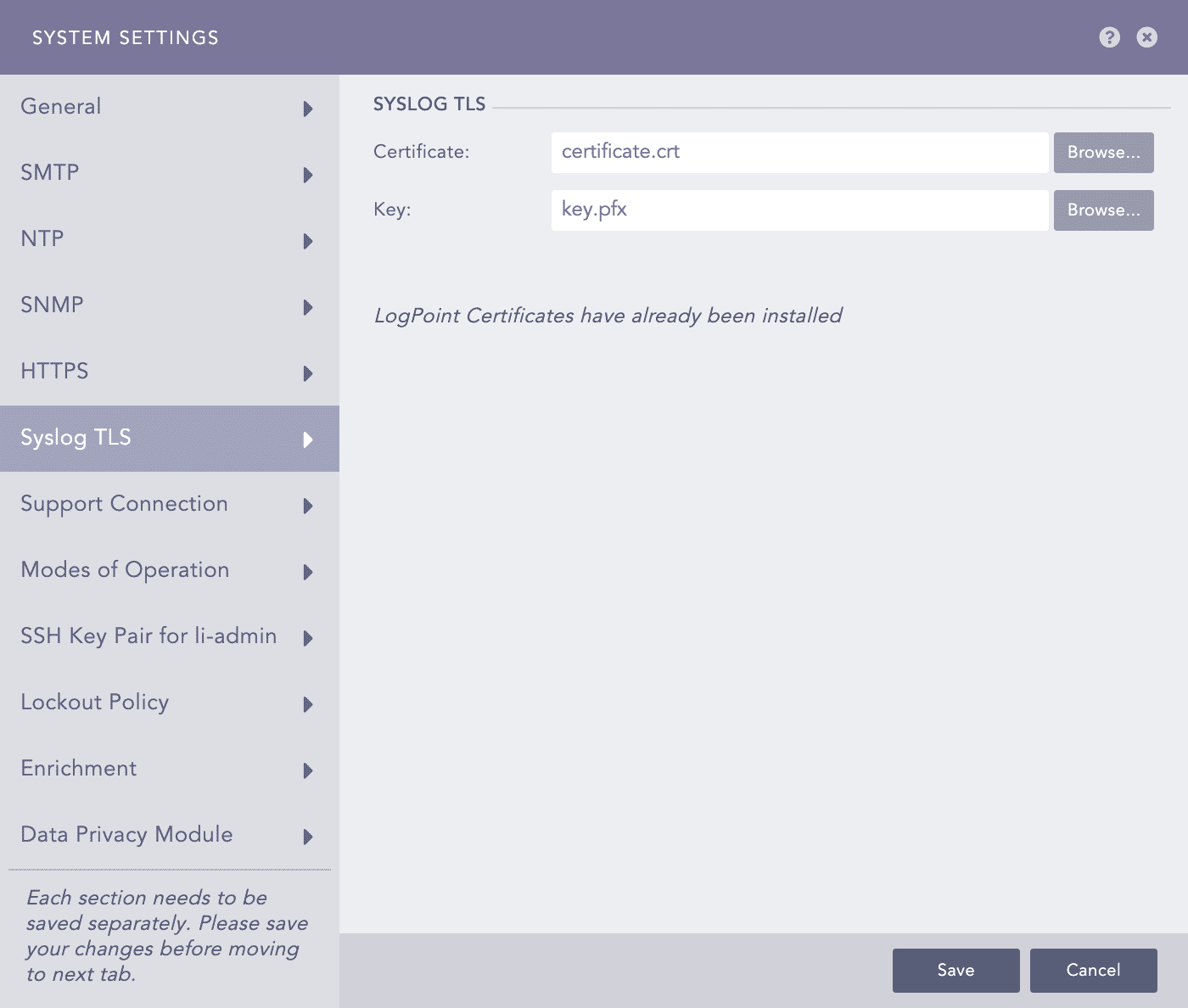
Syslog TLS - System Settings¶
Browse for the Certificate and the Key.
Click Save.
Note
Only the LogPoint Administrator users can add a certificate.
The certificate must be of PEM encoded x.509 standard.
The certificate file must have the CRT extension and the key file must have the KEY extension.
The Support Connection creates an encrypted end-to-end communication channel between the LogPoint and the LogPoint support. It is used by the LogPoint Support to understand, troubleshoot, and fix the issues on your deployment.
Before enabling support connection, make sure that your firewall is not blocking the connection from your LogPoint to the following:
Domain |
Port |
|---|---|
reverse.logpoint.com |
1193/UDP |
customer.logpoint.com |
443/TCP |
Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the Support Connection tab.
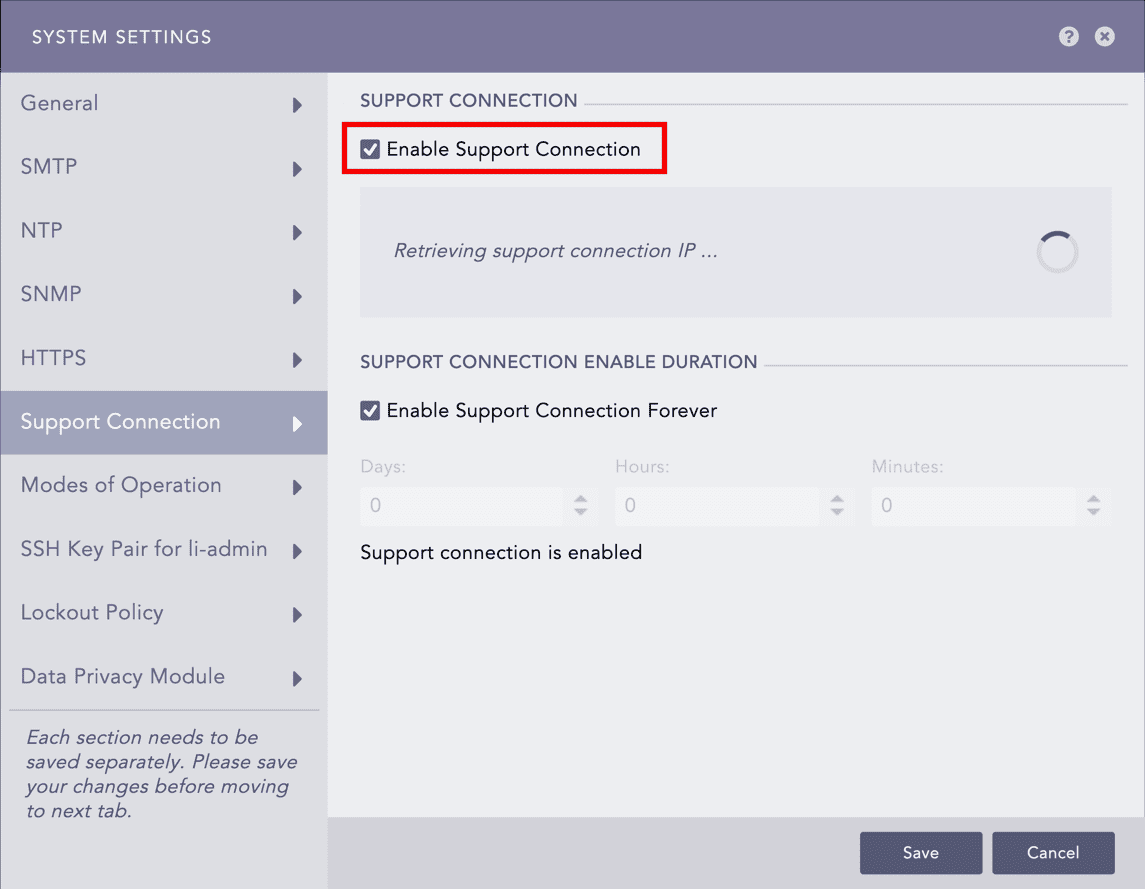
Enabling the Support Connection¶
Enable Support Connection. LogPoint starts retrieving the support connection IP.
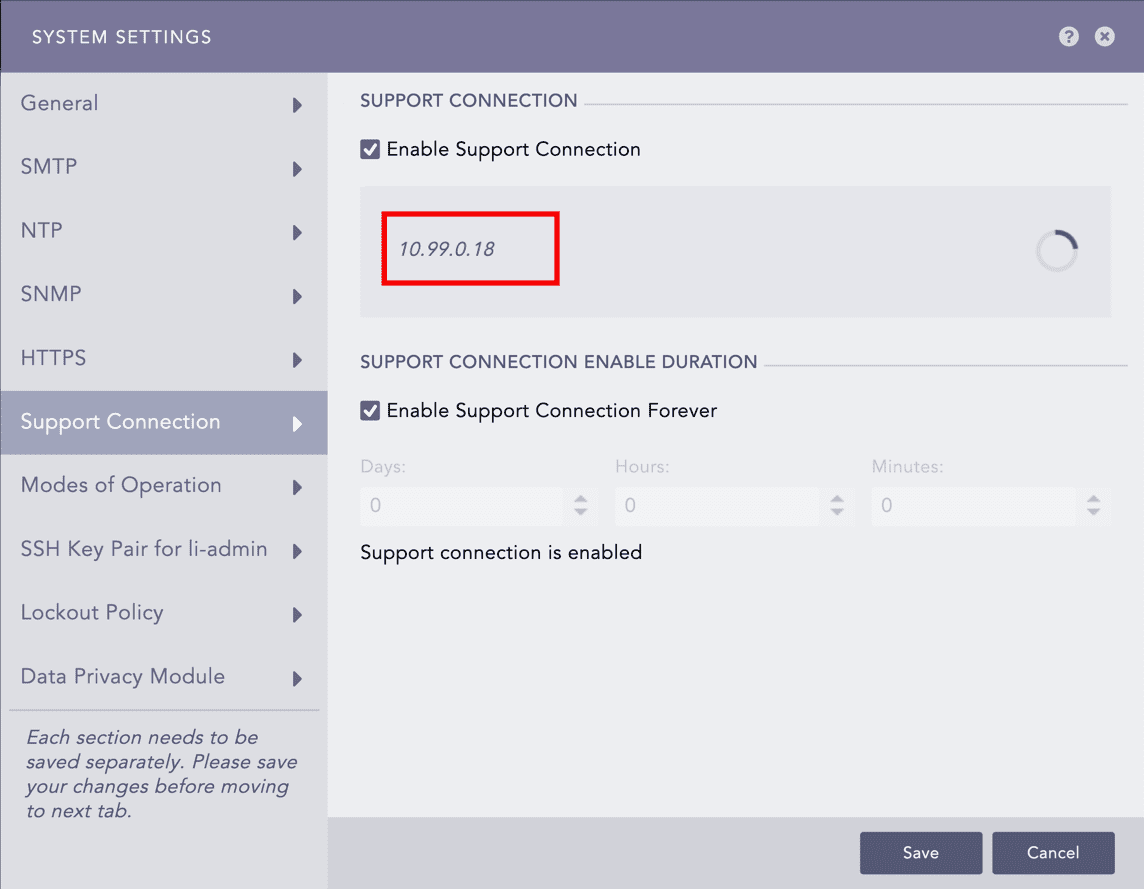
Retrieved Support Connection IP¶
Provide the retrieved support connection IP to the LogPoint Support team.
Provide the Support Connection Enable Duration. The support session expires after it exceeds the duration.
Note
Support connection never expires if you select 0:0:0 as the time duration, or Enable Support Connection Forever.
Click Save.
LogPoint can be operated in two modes using the Modes of Operation option.
LogPoint Collector
Syslog Forwarder
You can convert a regular LogPoint into either a LogPoint Collector or a Syslog Forwarder as per the requirement.
Modes of Operation - System Settings¶
LogPoint Collector is a LogPoint which collects logs from different sources, normalizes them using the signatures applied, and forwards them to a remote LogPoint. The remote LogPoint configures the sources and the storage locations for the logs.
Note
LogPoint Collector can only collect the logs. Therefore, it does not contain the Dashboards, the Search, the Report, and the LogPoint SOAR sections.
The name of each LogPoint node must be unique in a distributed deployment.
You need at least two LogPoint servers, one as the Collector and another as the Main LogPoint.
Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the Modes of Operation tab.
Configuring LogPoint Collector¶
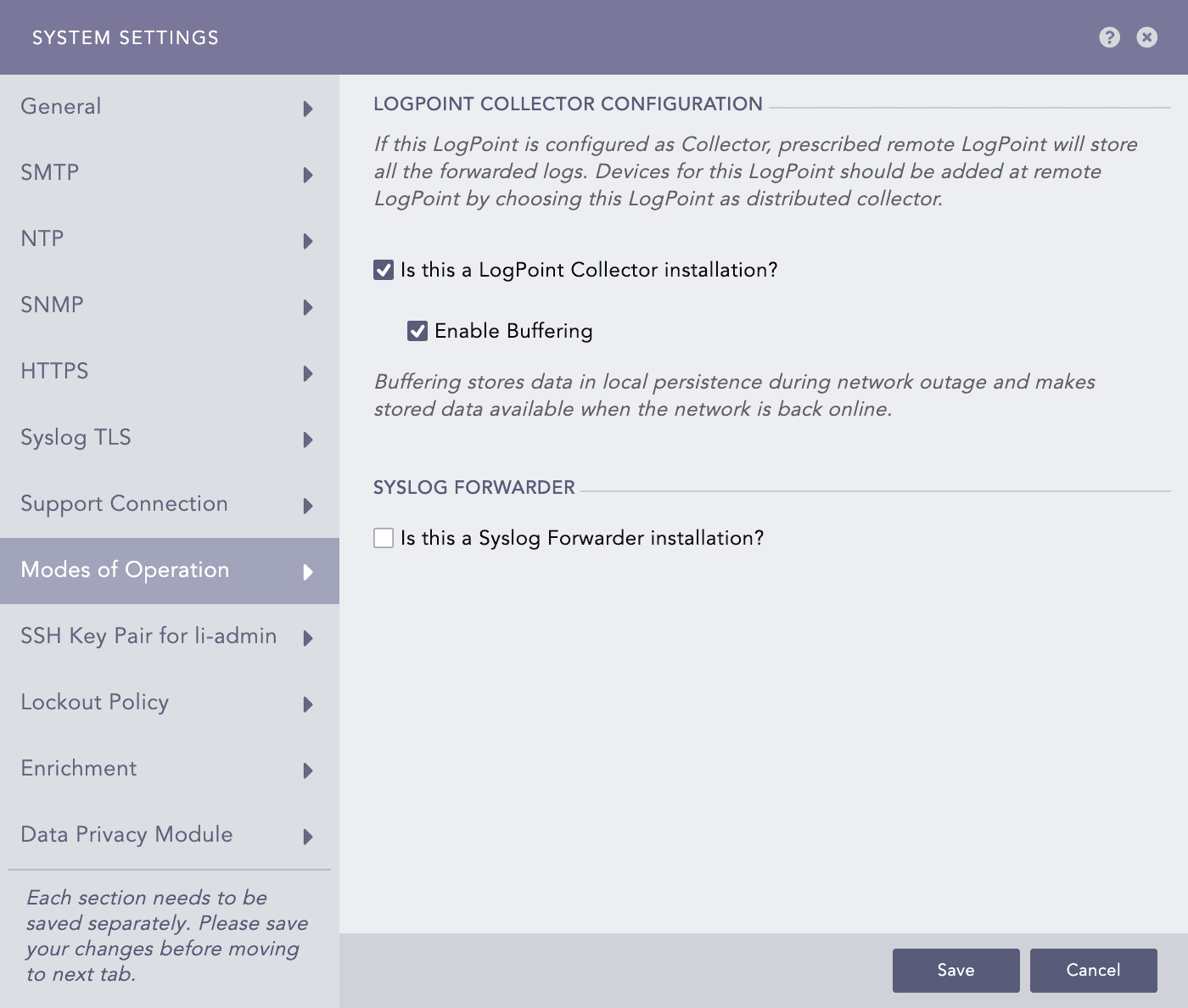
Mark the Is this a LogPoint Collector Installation? checkbox in the LogPoint Collector Configuration section.
Enable Buffering to store the data in local persistence during a network outage.
Note
By default, the logs are stored in the buffer for 7 days. However, you can change the default retention period by contacting the LogPoint Support and providing the desired retention period.
Click Save.
Switch to the Main LogPoint.
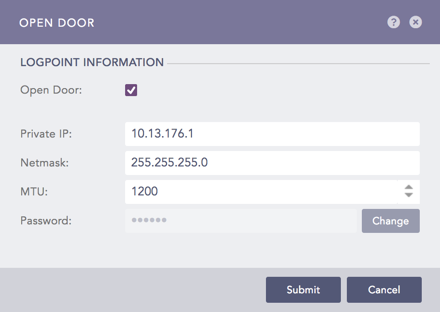
6.1. Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click Open Door.
6.2. Enable Open Door.
6.3. Note the Private IP and the Password.
Enabling Open Door¶
Switch to the Collector LogPoint.
7.1. Go to Settings >> Configuration from the navigation bar and click Remote LogPoint.
7.2. Enter the IP Address of the Main LogPoint, the Password, and the Private IP.
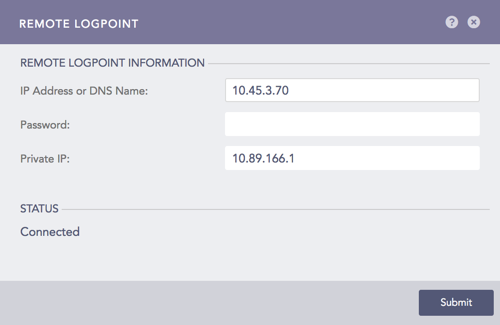
Configuring Remote LogPoint¶
The Collector is automatically added under Settings >> Configuration from the navigation bar and click Distributed Collector in the Main LogPoint. Activate it from the Actions column.
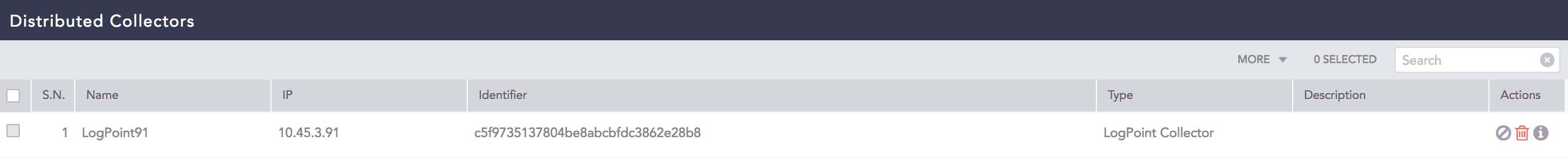
Configured Collector setting in Main LP¶
You can use the Collector to collect logs by adding it as a device in the Main LogPoint.
In the Main LogPoint, go to Settings >> Configuration from the navigation bar and click Devices.
Click Add.
Specify the Collector as a Distributed Collector.
To verify the connection between the devices, switch to the Collector LogPoint.
Go to View Devices.

Device Setting - View Devices¶
To distinguish logs collected and normalized through the Collector, you can use the system defined field, collected_at in the search query.
Note
If you disable the Collector, make sure that you remove it from the list of devices on the Main LogPoint.
If you change the password on the Collector machine from Settings >> Remote LogPoint, all the services of the Collector restart. The logs are not collected until the Collectors and Fetchers are up and running.
The Syslog Forwarder is a LogPoint which collects logs from different sources, normalizes them using the signatures applied, and forwards them to a remote LogPoint.
The Syslog Forwarder was developed in LogPoint to implement the concept of Air Gap. The Main LogPoints are usually located in high-security zones whereas the Syslog Forwarders and other devices are in low-security zones.
The detail process of configuring a Syslog Forwarder and steps to use it are described in detail below:
Go to Settings >> System settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the Modes of Operation tab.
Select the Is this a Syslog Forwarder installation? checkbox in the Syslog Forwarder section.
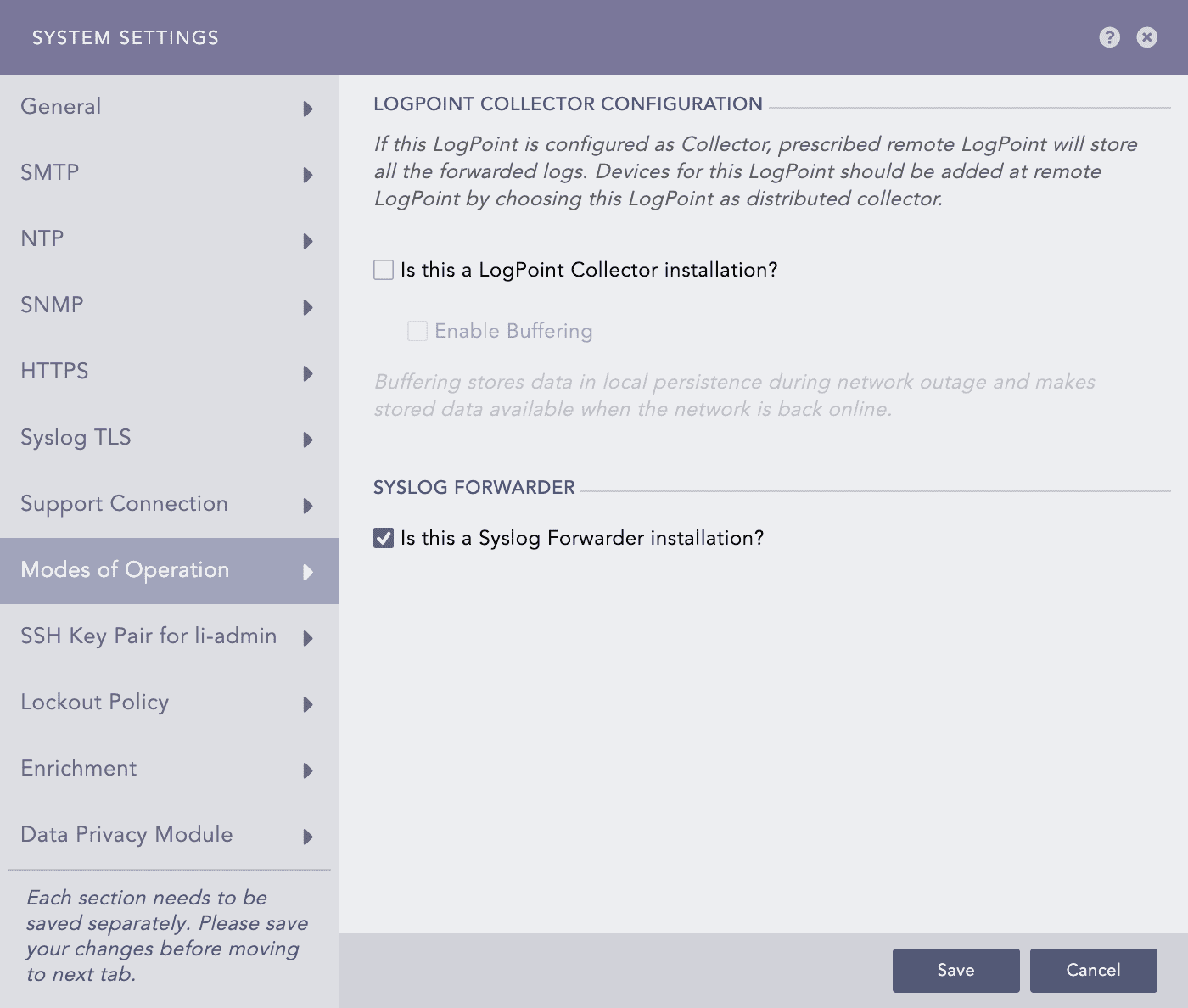
Modes of Operation - Syslog Forwarder¶
Click Save.

Logs from Syslog Forwarder¶
After converting a regular LogPoint to a Syslog Forwarder, you need to carry out the following steps to use it in the Main LogPoint:
Exporting a config file
Importing the config file
Adding targets
Adding devices
Exporting a config file
Switch to the Main LogPoint and go to Settings >> Configuration from the navigation bar and click Distributed LogPoints.
Add a Syslog Forwarder. Refer to the Adding a Syslog Forwarder.
Click the Export configuration icon in the Actions column of the concerned Syslog Forwarder.
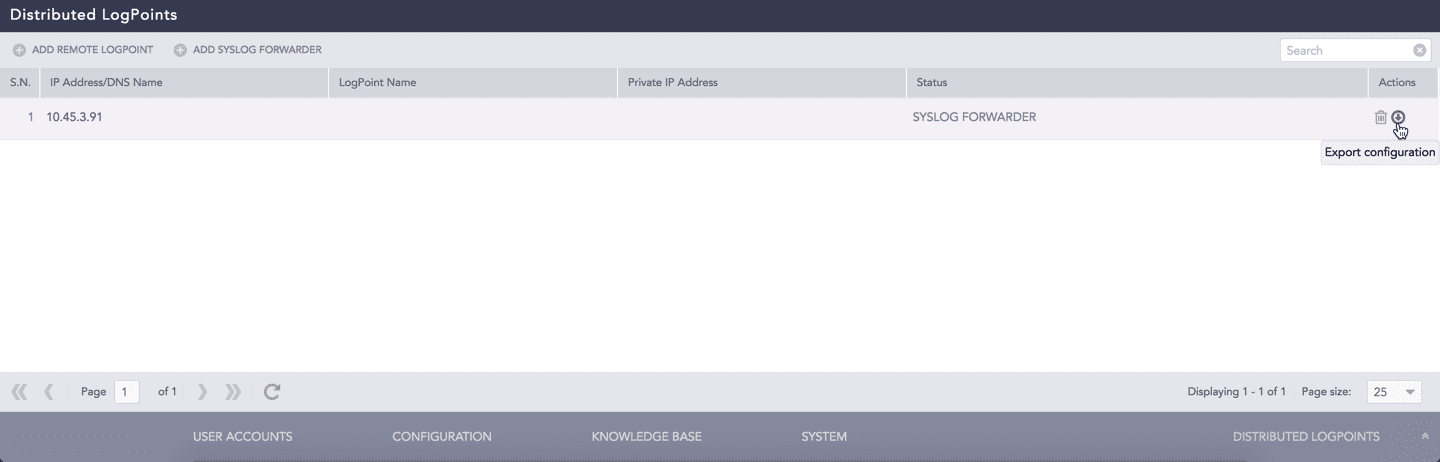
Export configuration¶
The config file is downloaded on your machine.
Save the config file.
Importing the config file
Switch to the Syslog Forwarder and go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click Sync.
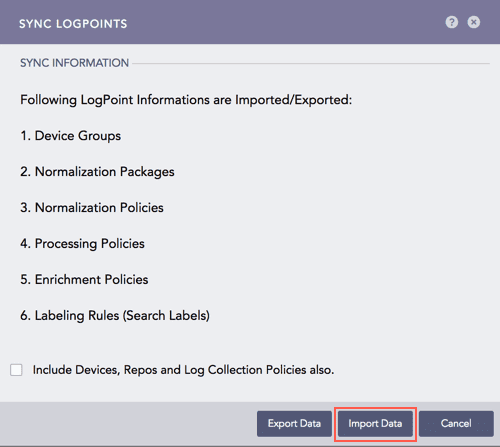
Sync config file¶
Click Import Data.
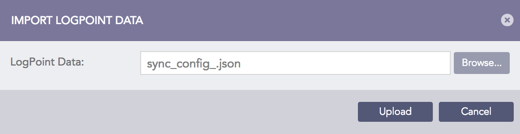
Import config file¶
Browse for the config file saved earlier.
Click Upload.
Adding a Target
On the Syslog Forwarder, go to Settings >> Configuration from the navigation bar and click Syslog Forwarder.
Click Targets to open the Remote Target panel.
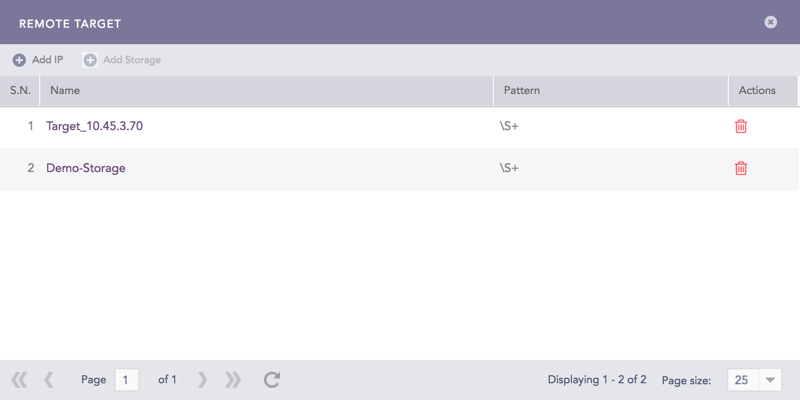
Remote Target¶
2.1. Add an IP (a remote syslog target).
2.1.1. Click Add IP to open the Add Remote Target panel.
2.1.2. Provide the Name and IP address of the target.
2.1.3. Specify the Pattern of the logs to be forwarded. If you do not specify a pattern, all the logs are forwarded.
2.1.4. Provide a Port number for the input port of the remote target machine.
2.1.5. Mark the Enable UDP checkbox to use the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). If you do not select the option, TCP is used.
If you Enable UDP, choose the UDP Size (In Bytes).
2.1.6. Click Submit.
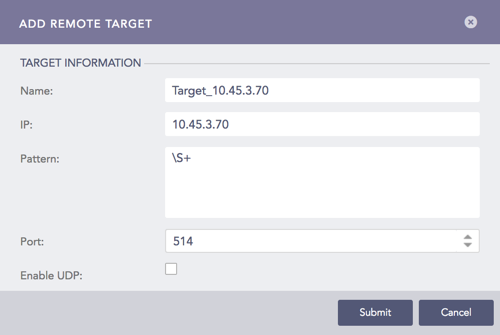
Add IP¶
2.2. Add a Remote Storage.
2.2.1. Click Add Storage to open the Add Storage Target panel.
2.2.2. Provide the Name of the storage.
2.2.3. Specify the Path to the remote storage. The format of the path should be:
//<IP Address>/<Path>/
For example: //192.168.2.247/storage/
2.2.4. Specify the Pattern of the logs to be forwarded. If you do not specify a pattern, all the logs are forwarded.
2.2.5. Provide the Username and the Password to access the remote storage target.
2.2.6. Click Submit.
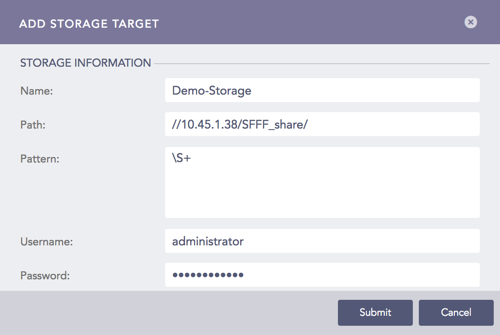
Add Storage¶
Note
You can add multiple Remote Targets but only one Remote Storage. The Add Storage option is disabled once the configuration for a storage target is complete.
For each IP added as the Remote Target, add the Syslog Forwarder in the respective target LogPoint.
Adding a Device
On the Syslog Forwarder, go to Settings >> Configuration from the navigation bar and click Syslog Forwarder.
Click Add to open the Configure Devices panel.
Note
The Device section lists all the devices configured as the Syslog Forwarder in the Main LogPoint.
Select devices by double-clicking on them.
Provide Remote Target(s). It can be a remote IP or a remote storage.
Click Submit.
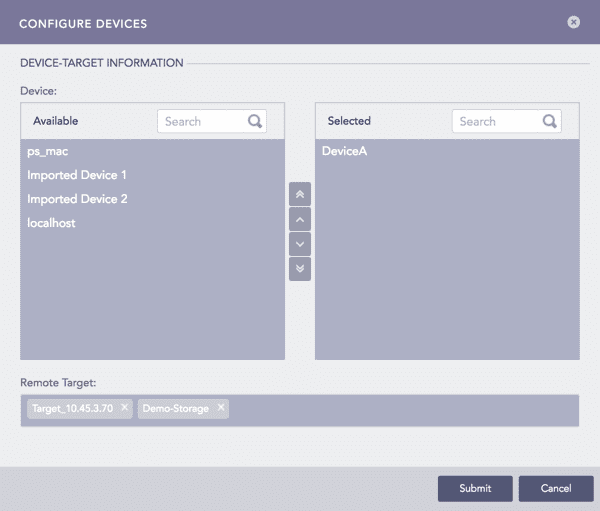
Configure Devices¶
A LogPoint Administrator can generate SSH certificates for the li-admin via the User Interface.
Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the SSH Key Pair for li-admin tab.
Provide a Pass Phrase.
Click Regenerate Key Pair.
The Lockout Policy lets you control user login and password security attributes. LogPoint locks your account for a specific lockout duration if you make multiple failed login attempts.
Lockout threshold: The Lockout threshold determines the number of failed login attempts that cause a user account to be locked. By default, the lockout threshold value is five. You can set a threshold value from 0 to 999, where 0 means a user account is never locked.
After three consecutive failed login attempts, you need to enter a CAPTCHA in addition to the username and password. If you make additional unsuccessful login attempts, that is, if you enter a wrong username, password, or CAPTCHA and reach the specified lockout threshold, your account is locked out for the specified lockout duration.
Lockout duration: The Lockout duration determines the number of minutes that an account remains locked out. By default, the lockout duration value is 30 minutes. After the lockout duration is over, you get one more login attempt. If this attempt fails, your account is locked for an additional specified lockout period. This process continues until you login with valid credentials. You can set a lockout duration value from 1 to 99999.
Note
After a user is locked out, a User Locked icon appears in the Actions column of the respective user under Settings >> User Accounts from the navigation bar and Users. The LogPoint administrator can unlock the locked users by clicking the icon.
Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the Lockout Policy tab.
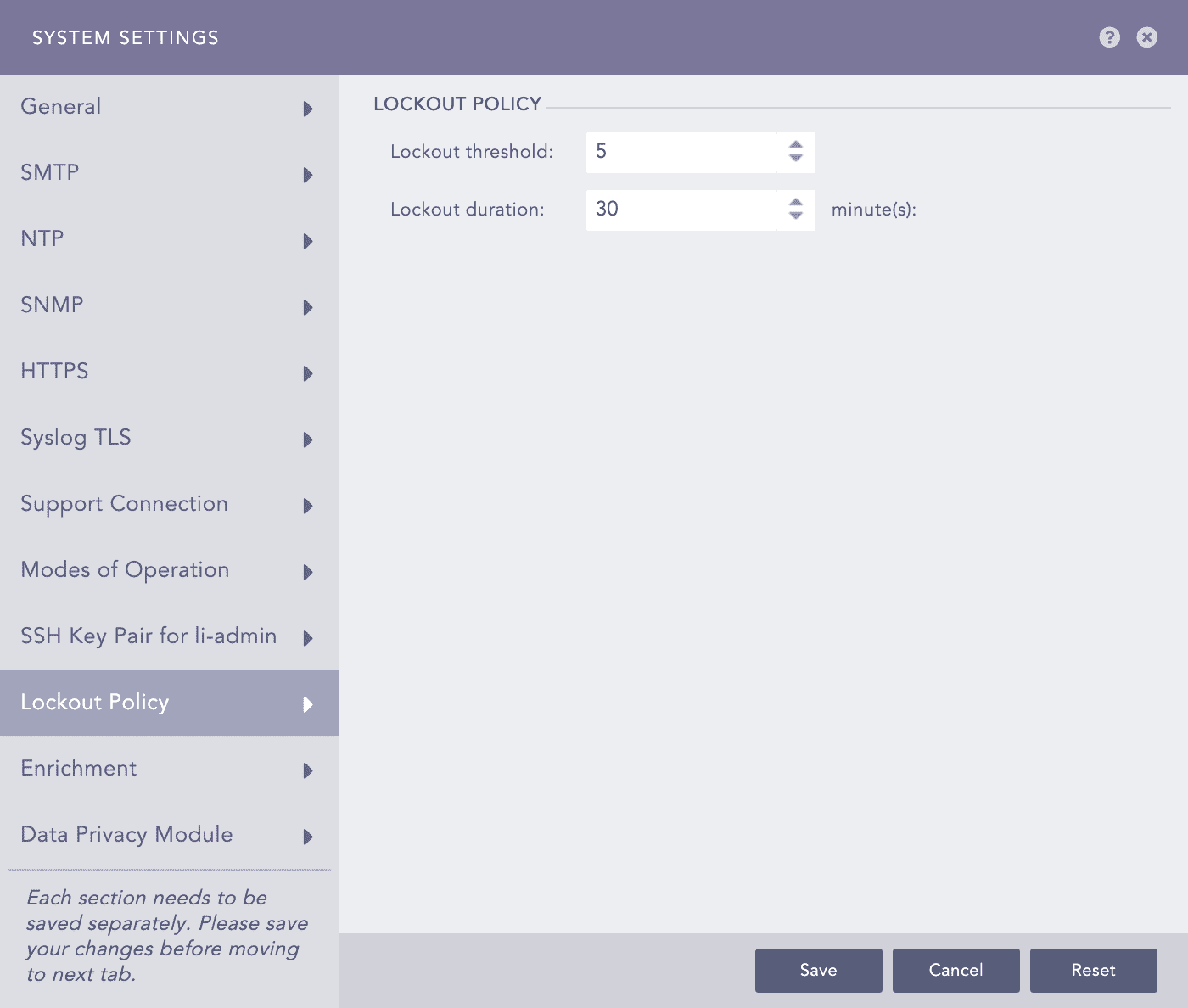
Configuring Lockout Policy¶
Provide the Lockout threshold from the drop-down list. By default, the lockout threshold value is set to 5.
Provide the Lockout duration (in minutes) from the drop-down list. By default, the lockout duration value is set to 30 minutes.
Click Reset if you want to reset the values to default.
Click Submit.
The enrichment process enhances and improves the usability of incoming logs by adding additional contextual information from enrichment sources. Enriched logs can help in routing, alerting, and making dashboards more relevant.
In LogPoint, the enrichment process starts with the extraction of event logs from source files. LogPoint checks whether each of the normalized logs are configured for an enrichment policy. If they are configured, logs are processed using the enrichment specifications provided in the enrichment policy.
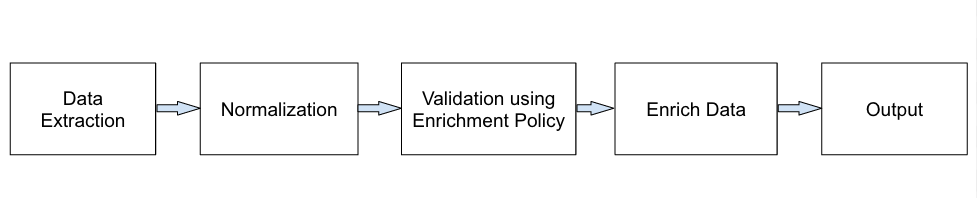
Enrichment Process Workflow¶
Enrichment can be performed in two modes: Standalone Mode and Enrichment Propagation Mode.
Before configuring Enrichment in either of the modes, it is necessary to configure some prerequisites in LogPoint. These essentials include Enrichment Sources, Enrichment Policies, Normalization Policies, and Processing Policies.
Note
Plugins associated with the enrichment sources need to be installed before adding an enrichment source. For example, if you need to add an ODBC enrichment source, the ODBC Enrichment Source plugin must be present in the LogPoint.
In the Standalone Mode, you need to add enrichment sources and perform the enrichment in the device itself.
Refer to the Enrichment Sources for details on adding enrichment sources.
In the Enrichment Propagation mode, you can set up multiple LogPoints to perform enrichment tasks. A LogPoint machine in this mode can be either an enrichment provider or an enrichment subscriber.
Enrichment Provider: Collects raw data and shares it with enrichment subscribers. It keeps a list of all the IP Addresses of enrichment subscribers.
Enrichment Subscriber: Receives enrichment data from an enrichment provider to create rules for the enrichment process. It also acts as a bridge between a LogPoint Collector and an enrichment provider.
Note
You must set up a Distributed LogPoint connection to configure LogPoint in the Enrichment Propagation mode.
The Enrichment Sources option in the Settings >> Configuration page is disabled in enrichment subscribers as they use the sources of an enrichment provider.
You can have any number of enrichment subscribers but only one enrichment provider. You can configure enrichment in the propagation mode in numerous ways. A single enrichment provider can be connected to:
A single enrichment subscriber
Multiple enrichment subscribers
A single enrichment subscriber connected to a LogPoint Collector
Multiple enrichment subscribers connected to multiple LogPoint Collectors
Go to Settings >> System Settings from the navigation bar and click System Settings.
Select the Enrichment tab.
Select Enrichment Propagation.
Select Enrichment Provider or Enrichment Subscriber as needed. If you select Enrichment Subscriber, choose a Subscription Source, which is the IP address of an enrichment provider from the drop-down menu.
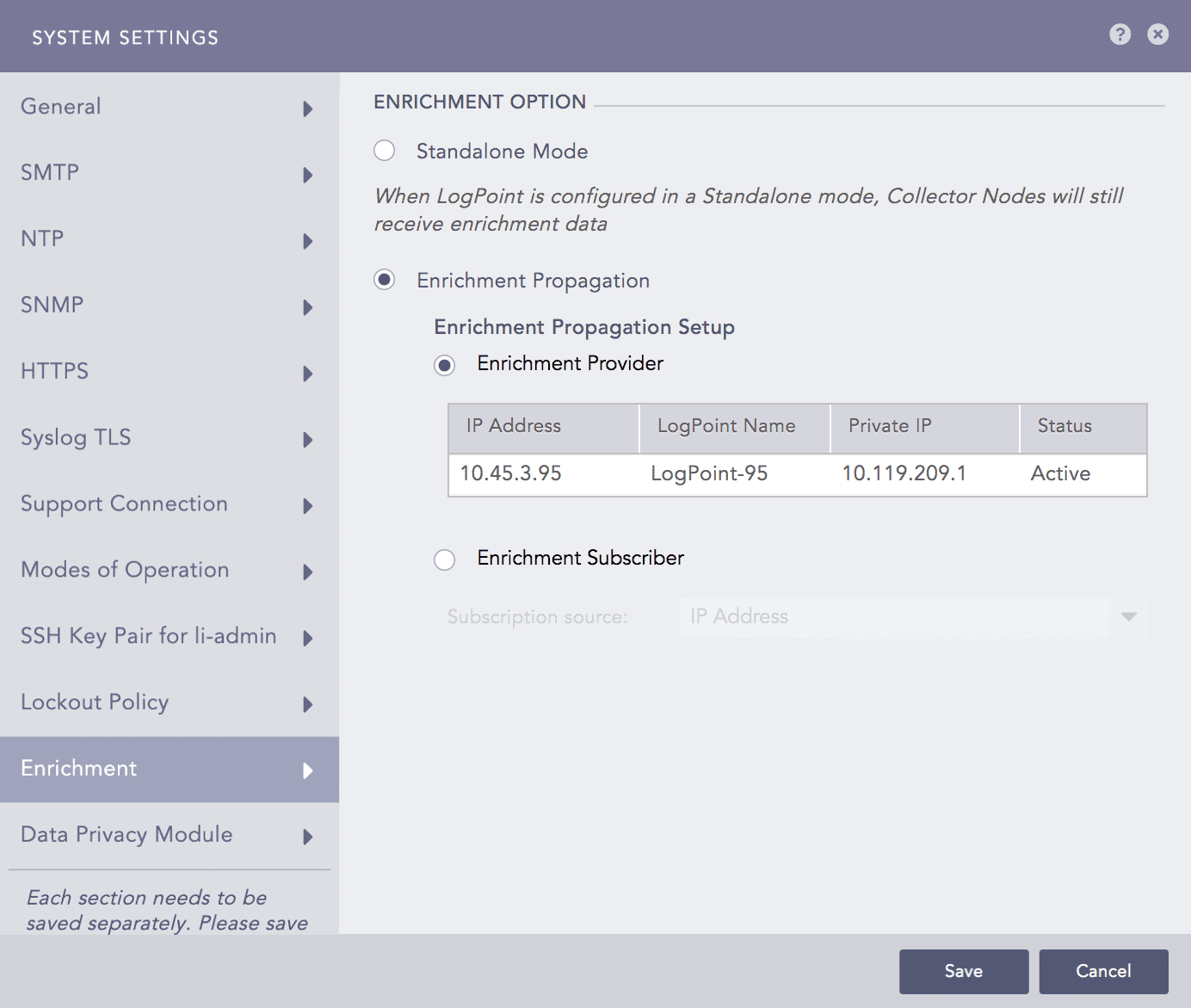
Selecting the Enrichment Propagation mode for Enrichment¶
Click Save.
Note
Make sure to configure an enrichment provider before configuring an enrichment subscriber.
Make sure to delete all the existing enrichment policies and their dependencies in a LogPoint before configuring it as an enrichment subscriber.
While removing the UEBA_ENRICHMENT_POLICY and Threat_Intelligence enrichment policies, remove the Threat Intelligence and UEBA PreConfiguration applications as well. After successfully removing the enrichment policies, manually install both the applications in the new enrichment subscriber.
The following scenario depicts an enrichment process in the Enrichment Propagation mode with a configuration of 2 machines: Machine 1 and Machine 2.
Select Enrichment Provider in Machine 1 and Enrichment Subscriber in Machine 2.

Configuring Machine 1 as an Enrichment Provider¶
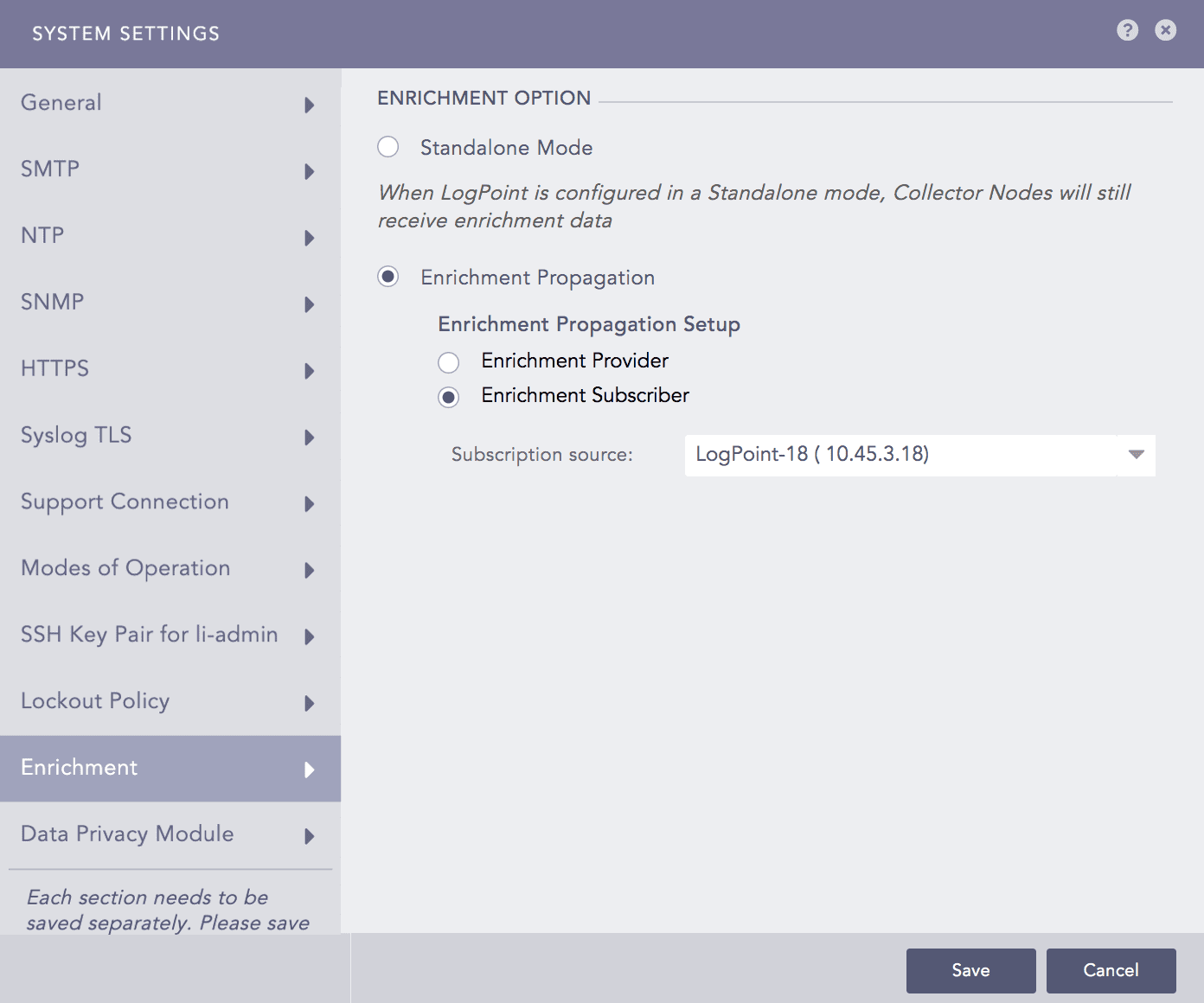
Configuring Machine 2 as an Enrichment Subscriber¶
Next, add a CSV Enrichment Source to Machine 1 using the data from the following CSV file.
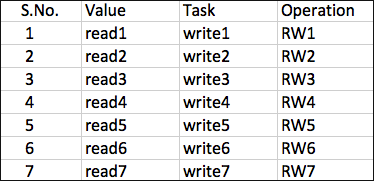
CSV File¶
After adding the source, add a normalization package containing log signatures to Machine 2. Refer to the Normalization Packages for details on adding normalization packages.
Furthermore, add a normalization policy, enrichment policy, and routing policy to Machine 2. Refer to the Normalization Policies, Enrichment Policies, and Routing Policies for details.
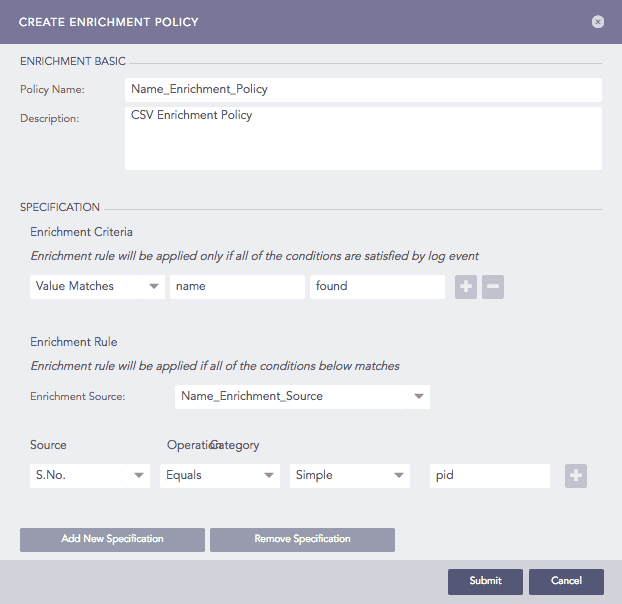
Adding an Enrichment Policy¶
Finally, add a processing policy to incorporate all the policies earlier created and add it to a device. Refer to the Processing Policies for details on adding processing policies.
Note
In the Standalone Mode, all the above tasks are performed in a single machine.
You can now see the enriched results in the search results of the enrichment subscriber.
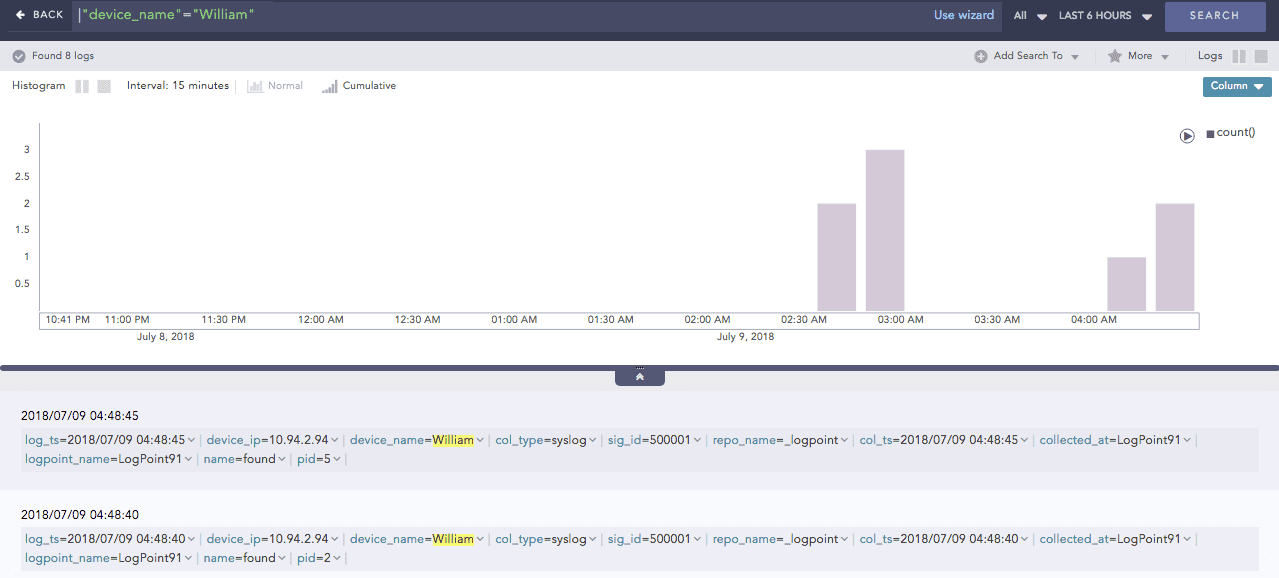
Non-enriched log result¶
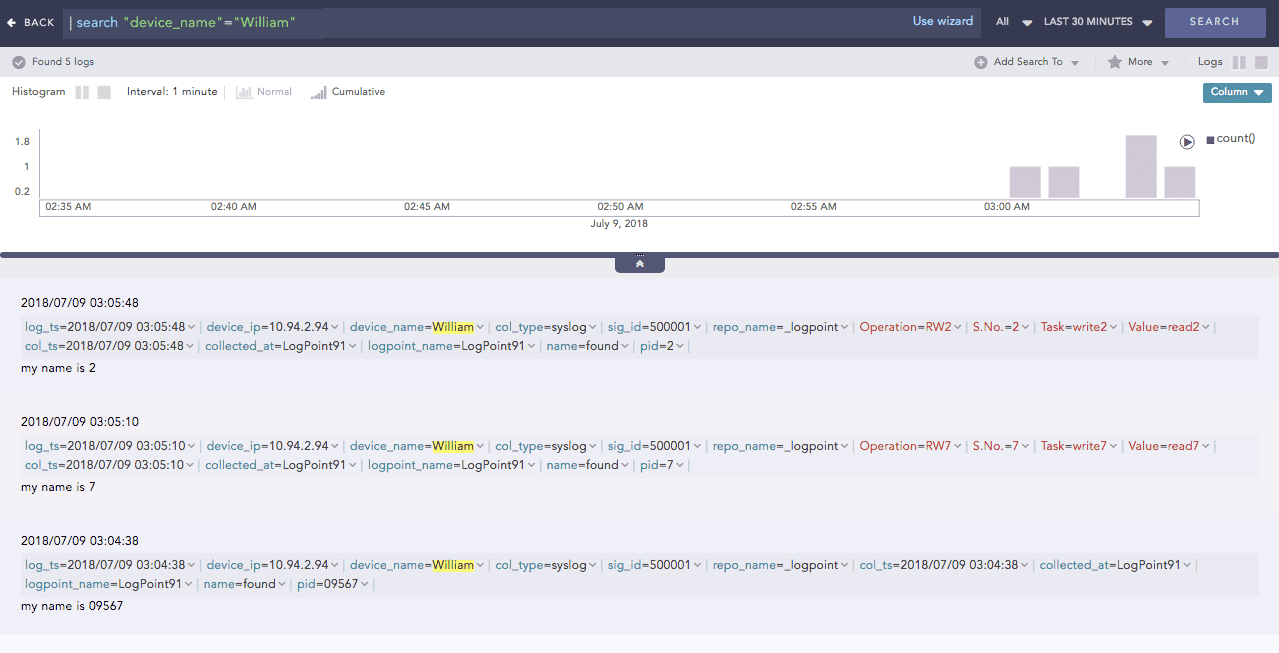
Enriched log result¶
Click the drop-down menu on the enriched fields to view the different actions.
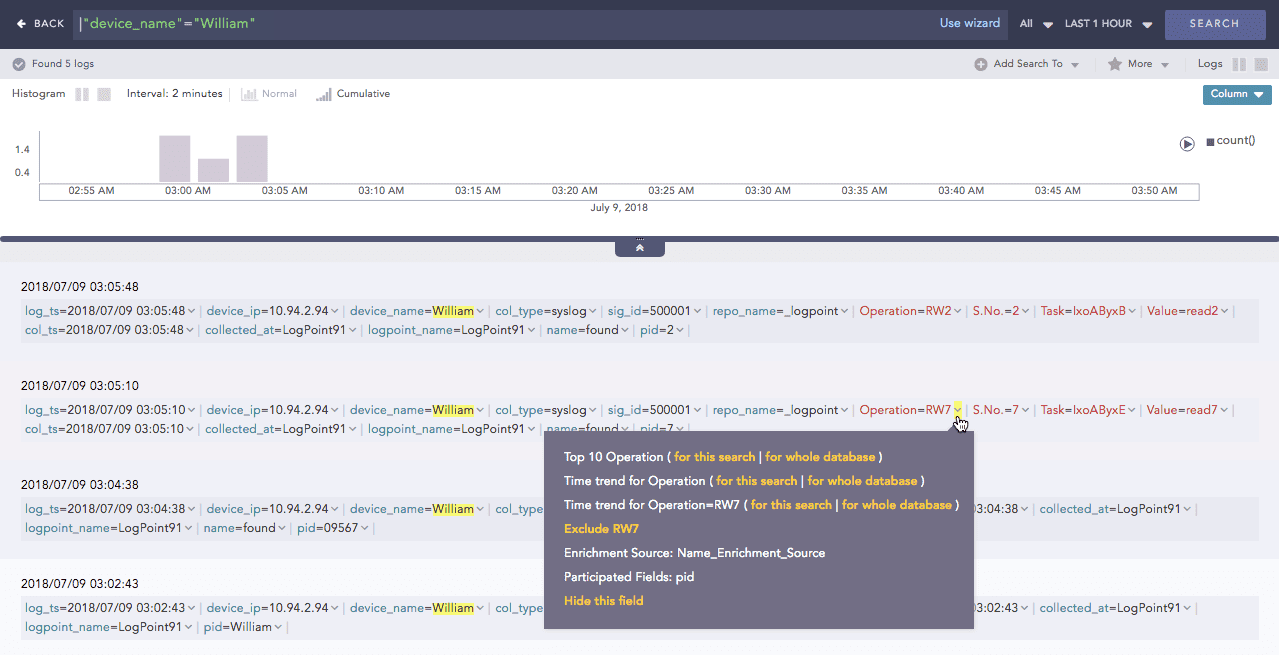
Actions in enriched results¶
Enrichment Source: Displays the information of the source file the enriched field belongs to.
Participated Fields: Displays the field of a log specified in the enrichment rule to enrich the log.
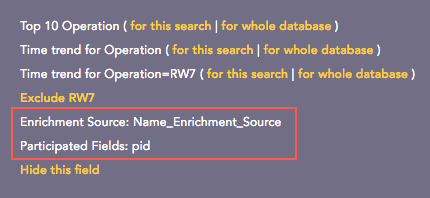
Actions¶
In the above example, the Participated Field pid has been specified in the earlier created enrichment rule. The enrichment rule matches the value of the pid field in the log to the S.No. field in the source and enriches the log.
We are glad this guide helped.
Please don't include any personal information in your comment
Contact Support